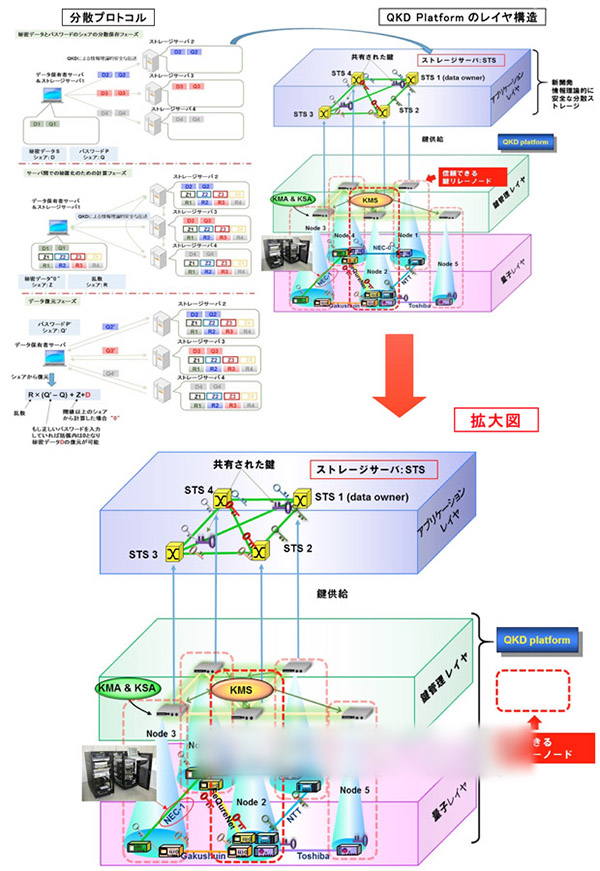
Schematic diagram of a distributed storage system built on the Tokyo QKD Network
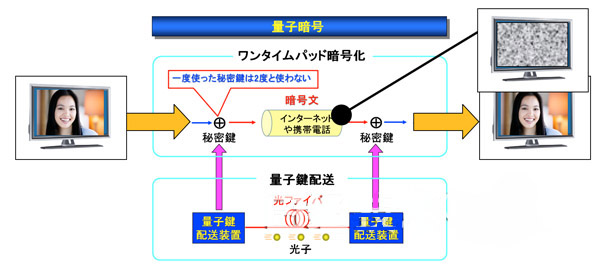
Summary of fully confidential communication using quantum key distribution (QKD)
The Japan Information and Communications Research Institute (NICT) announced on July 1, 2016 that in cooperation with the Tokyo Institute of Technology, it successfully completed a verification experiment for a distributed storage system in which user authentication, transmission, and preservation processes all ensure information theory security. It has been verified that it is possible to install a secure distributed memory that is free from the risk of information leakage regardless of how advanced the computer is in the future.
Most of the keys that are widely used on the Internet today are based on the time required for the computer to decipher it as a security basis. The ability of computers is increasing every year, and the security of destined keys will continue to decrease. For information that requires long-term confidentiality, such as national security information and genome information that will cause major problems after 30 years, establishing an information transmission and storage system (distributed storage system) that can guarantee security in the future is a top priority.
This time, in the Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) network used by NICT, Shamir's (k,n) threshold secret distribution method, which is a distributed storage protocol that can theoretically store data securely, is installed. In addition, a unique key distributed protocol is also installed together with the information theory security user authentication using only one key.
The QKD network transmits the photons modulated by the sender, and the receiver detects the status of each received photon and eliminates a bit that may be stolen (key distillation), thereby sharing an absolutely secure key between the senders and receivers. Once the modulated photon signal is subjected to a measurement operation, it will leave traces, so it can be seen whether it has been stolen. Shamir's (k,n) Threshold Secret Dispersion Method is a well-recognized protocol that can safely store data in information theory.
In the newly developed information theory security user authentication method, a new protocol has been developed that allows only one key to be remembered and the key can be securely authenticated in the future. Ordinary key authentication can only ensure the security of the calculation. The key can be calculated through a powerful computer.
In order to realize the above method, the storage servers need to transmit data with 10 times or more of the normal secret data, and accordingly, a more reliable and highly-designed QKD network is required. Researchers successfully validated the QKD network (Tokyo QKD Network) deployed on the optical fiber network in Tokyo circle used by NICT.
This part of the R&D has been supported by the innovative R&D promotion project (ImPACT) which is designed by the Japan General Scientific and Technological Innovation Conference. The research results were published on the electronic version of the scientific journal Scientific Reports of the British Nature Publishing Group on July 1, 2016 (UK time). (Reporter: Kudo Daisuke)
Komatsu Electrical Parts,Komatsu Forklift Parts,Excavator Electrical Parts,Quality Komatsu Electrical Parts
JINING SHANTE SONGZHENG CONSTRUCTION MACHINERY CO.LTD , https://www.sdkomatsudozerparts.com