Photocatalytic solar energy conversion is one of the effective ways to solve energy and environmental problems. As a new two-dimensional material, black phosphorene has many advantages such as layer-dependent direct band gap, wide spectral response, high carrier mobility, abundant active sites, etc., and has been widely used in recent years The field of photocatalytic solar energy conversion. However, the preparation conditions of black phosphorene are harsh, and the problems of fast photogenerated carrier recombination limit its development in the field of photocatalysis. Developing a gentle preparation method and constructing an efficient black phosphorus-based photocatalytic system is still a very challenging topic.
Recently, the team of Chen Yong, a researcher at the Research Center for Photochemical Conversion and Synthesis of the Institute of Physicochemical Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, used red phosphorus as a raw material to prepare a black phosphorus / red phosphorus heterogeneous junction photocatalyst in situ. The researchers found that the use of ethylenediamine, hexamethylenediamine, etc. as the reaction solvent can control the partial conversion of red phosphorus to black phosphorus under mild conditions. This method cleverly constructs a black phosphorus / red phosphorus heterophase junction, realizes the perfect interface contact between different semiconductors, promotes the separation of photogenerated carriers, and finally realizes the photocatalytic decomposition of water to produce hydrogen without any sacrificial reagent. In collaboration with Weng Yuxiang, a researcher at the Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, the researchers used time-resolved transient absorption spectroscopy to study the dynamic behavior of photo-generated carriers, revealing the Z-scheme of electron transfer from red phosphorus to black phosphorus during light excitation mechanism.
Related research results were published in the recent Angewandte Chemie International Edition, and were selected as hot articles. The first author of the article is Liu Fulai, a PhD student of the Institute of Physics and Chemistry, and the corresponding author is Chen Yong. The related research work was supported by the Class B strategic leading science and technology project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Chinese Academy of Sciences-Hong Kong University Joint Laboratory for New Materials Synthesis and Testing.
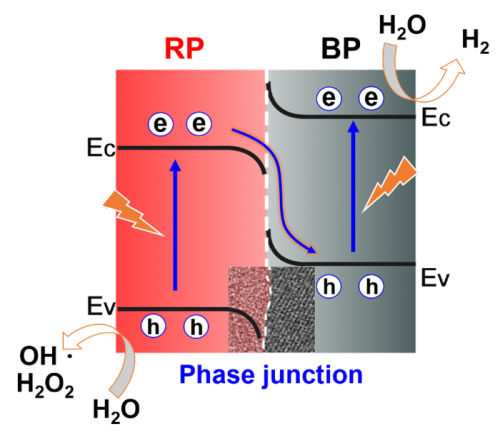
Schematic diagram of direct Z-scheme black phosphorus / red phosphorus heterophase junction
kaiping aida sanitary ware technology co.,ltd , https://www.kpaidafaucets.com