Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) diamond film coating tools on cemented carbide have shown excellent industrial application prospects. However, the biggest technical obstacle to the application of such tool materials is the low bonding strength between the deposited diamond film and the cemented carbide substrate. The main reasons are: 1 There is a difference between the thermal expansion coefficients (WC has a thermal expansion coefficient of 4×10-6 to 6.2×10-6/°C, and the thermal expansion coefficient of diamond is 1.2×10-6 to 4.5×10-6/°C). The solubility of 2C in the matrix Co is large. The diffusion coefficient of 3C in the matrix Co is high. The latter two factors promote graphite growth under CVD diamond conditions, interfere with diamond nucleation and growth, resulting in limited diamond nucleation and graphite deposition. If there is enough diamond nucleation, a continuous diamond film is formed, but because of the non-adherent graphite phase between the matrix and the diamond film, the interface is destroyed and the diamond film is always peeled off from the substrate. The reaction between Co in the surface of the substrate and C in the deposition gas source is the biggest technical obstacle to the adhesion of the diamond film to the cemented carbide tool. The key to enhancing adhesion is to remove Co from the surface of the substrate or inhibit its activity or motility. A common way to solve this problem is to reduce the amount of Co contained in the entire tool or apply an intermediate layer on the surface of the tool. However, the Co combined phase provides strength to the tool, and the overall reduction of the Co content of the tool will affect the performance of the cutting performance. The application of a suitable intermediate layer between the substrate and the diamond film can significantly improve the bonding properties therebetween.
This paper reviews various current researches on improving the bond strength between diamond films and cemented carbide substrates, including the preparation of fine-grained substrates, pre-treatment of substrates, optimization of process conditions for CVD diamond films, and in substrates and diamond films. The transition layer is applied between them, and the research prospects of depositing diamond film on cemented carbide are discussed in order to lay a foundation for the application of diamond film cutter.
1 Matrix material and its pretreatment
Matrix material KUNIO SHIBUKI pointed out that the WC particle size in WC-Co has a certain influence on diamond nucleation. Diamond is easy to deposit at the WC particle boundary. The finer the WC particle is, the smaller the size is. The higher the nucleation density of the diamond, the better the adhesion of the diamond film. 32. When the WC particle size is about 1 μm, the nucleation density of the diamond film is 9 × 106 cm -2 , and when the WC particle size is about 0.5 μm, the nucleation density of the diamond film is 5 × 107 cm -2 . .gif)
Figure 1 Diamond film deposited on a carbon-free carbide substrate
Surface de-Co treatment When chemically vapor-depositing a diamond film on a cemented carbide substrate, it is necessary to remove Co from the surface because Co is not conducive to the deposition of the diamond film. KUNIO SHIBUKI pointed out that the size of the pores generated on the surface of Co from the WC-Co substrate surface has a certain influence on the adhesion strength of the diamond film. When the hole size and the diamond particle size are almost the same, the adhesion strength of the diamond film is the best, and the flank wear of the diamond film cemented carbide insert is extremely small when the Al-10%Si alloy is cut.
After etching the substrate with a nitric acid solution (HNO3: H2O = 1:1) for 10 min, the amount of Co on the surface of the substrate was decreased by 0.2% [9]. MATaher grinds the WC-6%Co and WC-22%Co substrates with 1500 mesh diamond paper, then chemically etches them in a nitric acid solution (HNO3:H2O=1:3) for 10 min to remove the Co on the surface of the substrate, and then The substrate was subjected to ultrasonic treatment (diamond particle size less than 0.1 μm for 3 min) [10]. The energy scattering spectrum (EDS) test results show that the surface contains less than 1% Co. For substrates with a Co content of less than 1% on the surface, Co has no effect on the nucleation and growth of the diamond. At this time, the nucleation density of the diamond is about 108 cm-2. It is also pointed out that in order to obtain a higher adhesion strength of the diamond film, the roughness of the surface of the substrate should be in a certain range (Ra=0.06-0.25 μm).
IO.SAITO pointed out that the selective oxidation of Co on the surface of WC-Co with 2.5% CO-H2 plasma has the best properties of the diamond film prepared at a Co concentration of 10%, and its adhesion strength is 1.7 kgfmm- 2. The Vickers hardness is 8500 kgfmm-2. M. MURAKAWA et al. sputtered Co on the surface of WC-Co with Ar ion to reduce the content of Co to 0.8%, because the sputtering rate of Ar ion to Co and WC differed a lot, and the ratio of sputtering rate It is about 5:1.
Li Chengming et al. used excimer laser irradiation pretreatment on cemented carbide substrates, using the large difference in melting point of Co and WC (WC melting point is 2800 ° C, Co melting point is 1495 ° C), using high energy laser beam to generate selectivity Evaporation removes the Co of the surface layer of the YG6 cemented carbide, and the surface of the cemented carbide is roughened by laser surface modification, thereby causing a pinning effect on the diamond film, thereby further enhancing the bonding strength between the diamond film and the substrate.
Surface de-C treatment For the hot-pressed WC substrate, the carbon is first removed by a 2% O2-H2 plasma, followed by roughening the surface with diamond particles, and finally the diamond film is deposited by MWPCVD, as shown in FIG. The 2% O2-H2 plasma etches the surface of the WC substrate so that WC goes to C as W, and W is completely carbonized during diamond deposition, producing extremely fine WC particles (having a size of about 10 to 100 nm). Among them, the decarburization of WC and the carbonization process of W play an important role in the improvement of the adhesion strength of the diamond film due to the increase in the contact area between the diamond film and the extremely fine WC particles. As can be seen from Figure 1, the fine WC particles of the matrix invade into the diamond film. The adhesion of the diamond film is enhanced by the wedge effect of invading the WC particles.
2 CVD diamond film process conditions
Gas source types and gas concentrations MATaher et al. studied the deposition of diamond films with varying CH4 concentrations (1%, 3%, 5%, 7%, 9%). The results show that there is a certain relationship between the grain size of the deposited diamond film and the concentration of CH4. When the concentration of CH4 is 0.5% to 1%, the grain size of diamond is 5-11 μm; when the concentration of CH4 is 1% to 4%, The diamond grain size is 11 to 60 μm. The diamond film cemented carbide insert deposited at the CH4 concentration of 3% has the best mechanical properties.
IO.SAITO et al. studied the effect of CO concentration on diamond film deposition. It is pointed out that the diamond film prepared at a CO concentration of 10% has the best properties, the adhesion strength is 1.7kgfmm-2, and the Vickers hardness is 8500kgfmm- 2. The adhesion strength of the diamond film prepared at a CO concentration of 5% is 0.5 kgfmm-2, and the Vickers hardness is 10000 kgfmm-2; the adhesion strength of the prepared diamond film is 2.5 kgfmm-2 when the CO concentration is 50%. The hardness is 4000kgfmm-2.
M. MURAKAWA et al. pointed out that by using HFCVD method and using ethanol as a carbon source, a good quality diamond film layer can be obtained on a Co-rich WC alloy without special pretreatment of the cemented carbide substrate. Moreover, when the diamond film cutter is used for cutting an aluminum plate having a thickness of 2.5 mm, after punching 5×104, no abrasive grain adhesion and adhesion by the shear material fragments are observed on the diamond tip. The phenomenon.
Deposition temperature KUNIO SHIBUKI et al. pointed out that the adhesion strength of diamond film increases with the increase of deposition temperature, and the results are shown in the following table. When cutting Al-10%Si alloy, the flank wear of the diamond film cemented carbide insert is extremely small.
Diamond particle size/hole size and adhesion strength and deposition temperature .jpg)
3 Applying a transition layer deposits an intermediate layer between the WC-Co and the diamond film, and uses the intermediate layer as a diffusion barrier layer of C or Co, thereby solving the problem that the bonding strength between the deposited diamond film and the cemented carbide substrate is too low. The interfacial stress and film stress may be compensated for due to the difference in thermal expansion coefficient between the intermediate layer and the diamond film. A previous study was to deposit a compound of Si as an intermediate layer of diamond deposited on WC-Co. A diamond multilayer film structure developed by JM Albella et al. on a cemented carbide substrate is WC-8% Co/B/TiB2/B/diamond, wherein the total thickness of B/TiB2/B is less than 1 μm (thin B layer, 0.6 μm TiB2) , thin B layer), the best adhesion of the diamond film. The purpose of each part of the intermediate layer is different: 1 The initial B layer reacts with the Co on the surface of the cemented carbide tool to form Co2B and CoB. Therefore, the deposited first layer B is an effective measure for reducing the activity and mobility of Co on the surface of the cemented carbide tool. 2 Then, a layer of TiB2 is deposited on the first layer B or on the boride layer. For TiB2, CoB is thermodynamically stable, and the absence of B on the surface of the substrate enhances the bond between Co2B and CoB2 and TiB2. The role of TiB2 is to act as a diffusion barrier to separate C and Co. 3 The final layer B enhances the adhesion of diamond to TiB2. There are more chemical reactions between B and TiB2 and B and diamond than between TiB2 and diamond. Further, since B is deposited in an amorphous form, it can be used as a stress absorber. It is also noted herein that single layer B or single layer TiB2 is effective in increasing diamond nucleation density, but does not improve adhesion of the diamond film.
JM Albella et al. developed another multilayer film structure for improving the bonding strength between diamond film and cemented carbide substrate. The process has three steps: 1 CVD layer of discontinuous diamond core; 2 electrodeposition of a layer of Ni, Fix the diamond core deposited on the substrate first, and fill the entire gap of the diamond with Ni; 3 CVD diamond film; its structure is shown in Figure 2. 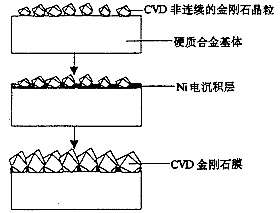
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of multilayer film structure 4 Prospects to improve the adhesion strength of diamond film on cemented carbide are mainly concentrated in the following aspects: 1 Select the appropriate matrix material. 2 The pretreatment of the surface of the substrate concentrates on the decarburization and decarburization treatment of the crystal seeds and the substrate which are sprayed with a diamond-like structure on the surface. 3 Optimize the film forming process conditions. 4 Apply a transition layer between the substrate and the diamond film. These aspects are effective to improve the adhesion strength of the diamond film to a certain extent, but so far, no fundamental solution has been found. A lot of work has been done on the first three aspects of research, but studies on the transition layer to improve the bonding properties between the matrix and the diamond film have just begun. Considering that the chemical vapor deposition (CVD) diamond film on the tool substrate has a low adhesion strength, and the bonding property between the metal Mo and the diamond film is good, the author proposes to use a multilayer film structure, that is, a cemented carbide substrate/Ni- Mo electrodeposited layer/Ni-Mo-diamond particles (having a particle size of about several micrometers) composite electrodeposited layer/chemical vapor deposited diamond film. A Ni-Mo deposited layer and a Ni-Mo-diamond composite electrodeposited layer are introduced as an intermediate layer between the diamond film and the cemented carbide substrate to improve the bonding property therebetween. Because of the deposition layer containing Mo, the nucleation density of diamond on the surface of the substrate can be greatly improved, and the addition of diamond particles can obtain several homoepitaxial growth microdomains on the surface of the substrate, thereby improving the bonding strength therebetween. Currently, this research is ongoing.
Parallel twin screw barrel,Filament Extruder Screw Barrel,Double Screw Extruder,Plastic Extruder Twin Screw
Zhejiang Zhongsu Screw Co., Ltd. , https://www.zhongsuscrew.com