Zhang Shougang Feng Lijuan Ru Caihua Tan Hui (Lutai Textile Co., Ltd. Shandong Zibo 255100)
Abstract: According to GB/T7573-2009 "Determination of pH value of textile water extract", the pH value of textiles was tested. The components of the influence results in the determination process were analyzed in detail, and the components were evaluated. display method. In the end, the source of uncertainty is mainly from the repeatability measurement, buffer solution, followed by the sample weighing and the volume of water.
Key words: T/C; CVC; knitting; dyeing and bathing; short process CLC number: TS 190.7 Document code: B Article ID: 1005-9350(2011)02-0044-02
The pH value of the textile is determined by testing the pH of the textile water extract and is a technical indicator for controlling the pH in the production process. If the additives in the textile printing and dyeing process are not fully washed, the pH of the fabric is too high, which exceeds the appropriate pH range of the skin, which will cause irritation to the skin, cause skin inflammation, and cause damage to the body's sweat gland system and nervous system. In order to protect human skin and prevent the invasion of pathogenic bacteria, the pH value of textiles is listed as one of the mandatory testing indicators. In GB 18401-2003 "National Textile Product Basic Safety Technical Specifications", the basic safety technical requirements of Section 5.1 Textile Products are shown in Table 1. Production, sales and import are prohibited for products that do not comply with this technical specification [1]. 
In this paper, according to GB/T7573-2009 "Determination of pH value of textile water extract", the uncertainty of textile pH was determined.
1.1 Measurement basis 1. Test part GB/T7573-2009 "Determination of pH value of textile water extract".
1.2 Measurement principle The pH of the textile water extract was measured at room temperature using a pH meter with a glass electrode.
1.3 Instruments and equipment EK-200i electronic balance (Japan AND); RAPID type constant temperature shock water bath (Taiwan Ruby); Thunder pHS-3C pH meter (Shanghai Jingke).
1.4 Sample Preparation High-density high-density cotton-dyed plaid fabric, while preparing 11 parallel samples, each weighing (2.00±0.05) g [2].
1.5 test process [2]
One sample and 100 mL of water were added to the stoppered flask, and the stopper was tightly capped. Shake well for a while to moisten the sample. The flask was placed on a mechanical shaker for 2 h ± 5 min. The pH meter is calibrated with two or three buffer solutions at the temperature of the water extract and the pH of each extract is tested. The first measurement is not recorded.
2. Mathematical model 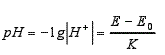
—H+—the concentration of hydrogen ions in the water extract;
Electromotive force of E-water extract in units of V;
Electromotive force of E0-buffer in V;
K-electrode constant.
3. Evaluation of uncertainty of measurement results [3]
3.1 Source of uncertainty a. Repeatability of measurement;
b. The uncertainty caused by the weighing of the electronic balance;
c. uncertainty caused by the measurement of the measuring cylinder;
d. The uncertainty obtained by measuring the pH value by the pH meter;
e. Buffer calibration The uncertainty produced by the pH meter.
3.2 Evaluation of uncertainty component analysis 3.2.1 Uncertainty u1 caused by repeated measurements
In order to obtain the uncertainty caused by repeated measurements, the samples were tested in parallel 10 times, and the results are shown in the following table; 
3.2.2 Uncertainty brought about by sample weighing u2 
3.2.3 Uncertainty of extraction water volume U3
The test cylinder is 100mL, according to the minimum scale value ±1mL, according to uniform distribution 
3.2.4 Uncertainty of the measurement by the pH meter u4
The pH meter calibration certificate gives a pH meter error of -0.01, a temperature compensation error of -0.01, and a resolution of 0.01. The uncertainty produced by the synthetic pH meter measurement is: 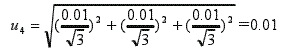
3.2.5 Uncertainty brought by buffer u5
The three buffers used in the standard pH meter (4.01, 7.01, 10.01) have an uncertainty of ±0.01. The standard uncertainty is: 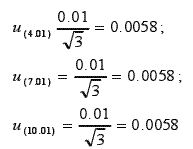
Since the pH meter is calibrated with these three buffers, the synthesis uncertainty is: 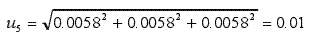
3.3 Relative standard uncertainty of pH of textile extracts urel (pH) 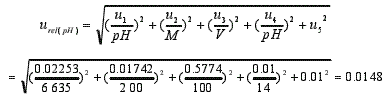
3.4 The standard uncertainty of the pH of the test sample extract is u (pH)
u(pH)=pH×urel(pH)=6.635×0.0148=0.0982
3.5 Test sample extract pH expansion uncertainty U extension Select the confidence probability 95%, including the factor K = 2, then U expansion = u (pH) × 2 = 0.0982 × 2 = 0.2
3.6 Results The pH of the textile extract was 6.6 ± 0.2. Its extended uncertainty is 0.2, which is obtained by the product of the standard uncertainty of 0.09788 and the inclusion factor k=2, and its confidence probability is approximately 95%.
4. Conclusions The uncertainty factors of the pH value of the extract in textiles are mainly due to the uncertainty caused by repeated measurements and the buffer solution calibration pH meter, followed by the sample weighing and the volume of water. In the inspection, it is necessary to strictly follow the specifications to improve the stability of multiple tests, and to use buffer solutions and gauges with higher precision.
5. References
[1] National Standard of the People's Republic of China, National Basic Technical Specification for Textile Products, GB18401-2003.
[2] National Standard of the People's Republic of China, Determination of pH Value of Textile Water Extract [S], GB/T7573-2009.
[3] Ni Yucai. Evaluation of Practical Measurement Uncertainty. Beijing: China Metrology Press, 2010.
Piping Accessories,Piping Tool Accessories,Pipe Fitting Accessories,Automatic Suction Water Filter
Jiangsu Hida Marine Valve Co., Ltd , https://www.haidavalve.com