Abstract: The optimum conditions for the application of pectinase were obtained through experiments: acid pectinase A pH value 3~5, temperature 30~60°C; alkaline pectinase B pH value 7~9, temperature 40~60°C Under the conditions of the process, the scouring effects of the two enzymes were compared, and two pectinase activities and SDS-PAGE electrophoresis were determined, and their refining characteristics were analyzed. The results showed that the alkaline pectinase B had a small molecular mass. The specificity of the enzyme is stronger, and the cotton fiber pectin substance removal has better effect [alkaline pectinase B 0.025% (owf), JFC 0.2g / L, pectin removal rate > 70%.
Biological enzyme refining is an ecological dyeing and finishing technology. It has the advantages of mild conditions, low water consumption, low organic pollutants for discharging waste water, and small damage to cotton fibers. It is a kind of textile clean production process with energy saving, pollution-free and pollution-free. Researchers from various countries have successively investigated the scouring effects of pectinase, cellulase, protease, lipase and their complex enzymes on cotton fabrics. The results show that pectinase is an ideal enzyme preparation for enzymatic refining. Currently, The pectinase used for cotton fabric refining has acid pectinase A and alkaline pectinase B, but the difference between the two types of enzyme refining effects and the influencing factors are still unclear. This paper optimizes the acid pectinase A and basic fruit. The application conditions of gelase B and the pectin removal rate were compared with the scouring effect of the two enzymes. The effect of surfactant on the enzymatic scouring effect was analyzed. By detecting the molecular mass of the enzyme, it was explained from the perspective of enzyme specificity and molecular diffusion. The reason for the difference in the effects of the two types of enzyme refining.
1 test
1.1 Materials and instruments
Pure knit cotton: 26S 1 × 2 cotton 1 × 1 rib 33cm / 50g (370 ± 5) g / m2. Drugs: acid pectinase A (British AB), alkaline pectinase B, pectinase C ( Alkaline pectinase B purified) (Norwegian Novozymes), fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether (JFC), D-galacturonic acid (Sigma, USA), ammonium oxalate, carbazole, absolute ethanol ( Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd.).
Instrument: HH-S6 digital display constant temperature water bath (Jincheng Guosheng Experimental Instrument Factory, Jintan City, Jiangsu Province), 754 micro-computer UV-visible spectrophotometer (Shanghai Chengguang Instrument Co., Ltd.), electrophoresis instrument and vertical electrophoresis tank (Bio -Rad company), Rapid dyeing prototype (LABORTEXCO., LTD).
1.2 enzyme refining process
With appropriate amount of pectinase, JFC, in a certain pH, temperature water bath for 30min, bath ratio 1:20, then hot water wash (80 ° C, 10min), cold water wash (25 ° C, 10min).
1.3 test
Pectinase activity: determined by DNS method to analyze the effect of pectinase on temperature and pH. Pectinase activity unit (U) definition: 1mgD-galacturonic acid required for 1min under certain pH and temperature conditions The amount of enzyme; the content of D-galacturonic acid was determined by reducing sugar method. The removal rate of pectin: the effect of enzyme scouring was evaluated by measuring the removal rate of pectin, and the removal rate of pectin = (1 - W1/W0) × 100%. In the formula, W1 is the residual amount of pectin (g) after scouring, W0 is the amount of pectin on unrefined fabric (g); pectin content: using ammonium oxalate extraction - carbazole colorimetric method.
2 results and discussion
Drawing of 2.1D -galacturonic acid standard curve
The D-galacturonic acid content was tested by the reducing sugar test method, and the D-galacturonic acid standard curve was drawn. The optical density value of 540 nm was plotted on the ordinate and the D-galacturonic acid content was plotted on the abscissa. For the curve, the standard curve equation is y=1.666 x +0.131, and the correlation coefficient R2 is 0.9994.
2.2The effect of pH and temperature on the amount of pectinase reducing sugar
2.2.1 pH value
It can be seen from Fig. 1 that the pH value of 3~5 is the optimum range of acid pectinase A. After the pH value is greater than 5, the enzyme activity of acid pectinase A decreases rapidly, so the acid pectinase A should be The pH value is 3~5; the pH value is 7~9 is the optimum range of alkaline pectinase B. When the pH value is greater than 9 or less than 7, the enzyme activity of alkaline pectinase B decreases rapidly, so alkaline Pectinase B should be used at a pH of 7~9. 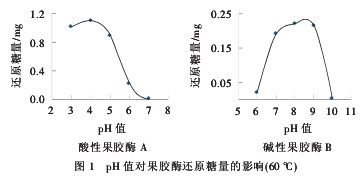
2.2.2 Temperature
It can be seen from Fig. 2 that 30~60 °C is the optimum temperature range of acid pectinase A. After more than 60 °C, the enzyme activity decreases rapidly, so the acid pectinase A should be used at not more than 60 °C; The optimum temperature range of pectinase B is 40~60°C, and the enzyme activity is significantly decreased over 60°C. Considering the effect of temperature on the enzyme catalytic reaction, the enzyme protein inactivation is caused by high temperature, and alkaline pectinase B should be 40. ~60 °C use. 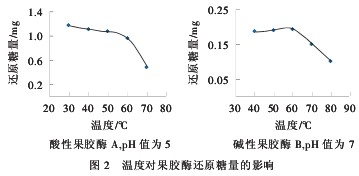
2.3 pectinase enzyme activity
It can be seen from Table 1 that the enzyme activity of acid pectinase A is twice that of alkaline pectinase B under the conditions of suitable temperature, pH value and pectin substrate. 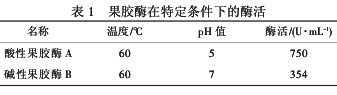
2.4 pectinase refining effect
It can be seen from Fig. 3 that when the amount of acid pectinase A is 0.01%~0.50% (owf), the removal rate of pectin is maintained at about 20%; and when the amount of alkaline pectinase B is 0.05%, pectin is used. The removal rate is over 80%. According to the experimental experience and literature, when the pectin removal rate reaches 70%, it can meet the needs of refining processing. At this time, the amount of alkaline pectinase B is 0.025%. The reasons are as follows: (1) Under alkaline conditions, pectinase and surfactant can synergistically produce saponification and emulsification, which can effectively remove pectin, wax and other impurities, thereby enhancing the refining effect; (2) alkaline pectinase B is refined for cotton fabric, Its specificity and pertinence are stronger; (3) Alkaline pectinase B has lower molecular mass and stronger permeability, and it is more likely to be in contact with pectin, and the pectin removal rate is higher. 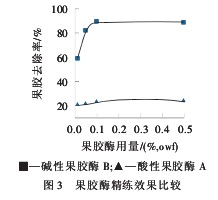
The following analysis of the effect of penetrant on the scouring effect of alkaline pectinase B and protein electrophoresis test to analyze the molecular mass of the two enzymes to further confirm the (3) analysis.
2.5 Effect of penetrant alkaline pectinase B
It can be seen from Fig. 4 that the pectin removal rate increases with the increase of the amount of nonionic surfactant JFC. When the JFC dosage reaches 0.2 g/L, the alkaline pectinase B has a stable pectin removal rate. About 75%, considering the most effective amount, the optimum amount of JFC is 0.2g/L. The effect of nonionic surfactants such as JFC on alkaline pectinase B is attributed to the improvement of fabric wettability. And the mobility of the enzyme on the fabric, so that the enzyme is easy to desorb and the accessibility to the substrate, which facilitates the movement of the enzyme to the catalytic reaction, thereby increasing the activity of the enzyme. However, when their critical micelle concentration is exceeded, The activity of the enzyme is reduced. When the JFC is not added, the pectin removal rate is about 20%. It indicates that the diffusion of the enzyme molecule in the cotton fiber is essential for the removal of pectin, if the molecular mass of the acid pectinase A is Large, molecular diffusion is blocked, and its chance of contact with the substrate is reduced, which may lead to high enzyme activity and low pectin removal rate. 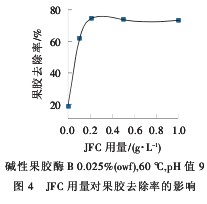
2.6 pectinase electrophoresis
As can be seen from Fig. 5, the acid pectinase A is in a band with a molecular mass of 50 kDa, while the alkaline pectinase B band is more. Compared with the pectinase C band type, the molecular mass of the active ingredient is 30kDa, consistent with the reported pectinase molecular mass of 20~60kDa, indicates that alkaline pectinase B has smaller molecular mass than acid pectinase A, which is beneficial to the diffusion of enzyme protein molecules, and can further improve alkaline pectinase. B's refined effect. 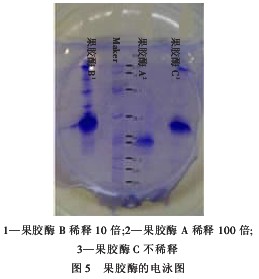
3 conclusions
The optimum pH value of acid pectinase A is 3~5, the optimum temperature is 30~60°C; the optimum pH value of alkaline pectinase B is 7~9, and the optimum temperature is 40~60°C. Under the optimum conditions, the alkaline pectinase B has a much higher removal rate of pectin than the acidic pectinase A. The reasons are: (1) alkaline conditions are beneficial to the removal of pectin substances; (2) alkaline The pectinase B molecular mass is small, which is beneficial to increase the rate of pectinase molecules diffusing through the liquid interface layer to the fiber surface and into the fiber; (3) its specificity for cotton fiber pectin substances. Alkaline pectin The removal rate of pectin of enzyme B at a low dosage (about 0.025%) and short time (about 30 minutes) can meet the production requirements. Therefore, the biological enzyme refining should be based on alkaline pectinase B, supplemented by other auxiliaries. This is beneficial to improve the refining effect and reduce the production cost.
Pull Out Kitchen Faucet,Pull Out Sink Faucet,Brass Kitchen Mixer,Chrome Pull Out Kitchen Faucet
kaiping aida sanitary ware technology co.,ltd , https://www.aidafaucets.com