-
Easy to tighten & "International Standard Parts" " Yongnian Fastener Technology and Application Training Conference" notice
A A STM
The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM ) was formerly known as the International Association for Testing Materials (IATM ). In the 1880s , in order to solve the opinions and differences between buyers and suppliers in the process of buying and selling industrial materials, it was proposed to establish a technical committee system, where technical committees organized representatives from various fields to participate in technical seminars to discuss and resolve relevant material specifications. Controversial issues in the test procedures.
There are a total of 2004 technical subcommittees under the ASTM technical committee. There are 105 817 units participated in the ASTM standards development work, the main task is to develop the characteristics and performance standards in the field of materials, products, systems, and services (rather than develop specific shape fastener products, size standard), test methods and Program standards to promote the development and promotion of relevant knowledge.
 B B S
BS standards developed by the British Standards Institute (Britain Standard Institute, referred to as BSI) British Standards. BSI is an unofficial institution with a high reputation internationally. It was established in 1901 and is the world's first national standardization body. It is not controlled by the government but has received strong support from the government. BSI develops and revises British standards and promotes their implementation.
Within the standard of BS fasteners, there are three kinds of common mechanical threads: BSW , UN and M. The measuring units are inch and mm , so the British standard is not necessarily all British.
 Type C tank
The slot type of the fastener, relative to the mounting of the hex head, is also referred to as the inner wrench. Considering the processing, installation efficiency, installation torque, anti-corrosion after installation, anti-theft and other reasons, the design of a slot, hexagon socket, plum blossom groove, various word composite groove, various anti-theft slots.
 D D IN
German Institute for Standardization (DIN) is Germany's largest private nonprofit organizations standardize broadly representative, was established in 1917 and headquartered in the capital Berlin. Germany is one of Europe's Committee for Standardization CEN (European Committee for Standardisation) of 18 member states, DIN plays an important role in the CEN, CEN one-third of the Technical Committee chaired by the Secretary of State of Germany. DIN constantly considers international and European trends in the development and revision of standards, so the number of standardized projects it operates is also changing year by year. In 1984 , 5% of the DIN standardization projects were international standardization projects, 12% were European standardization projects, 83% were purely national standards, and by 1994 , international standardization and pure German standardization each accounted for 25% , while the European standardization part It is 50% . Over time, more and more European standard ENS (Europaeische Norms) has been adopted by Germany as the new DIN EN standard instead of the original DIN standard. For example , nearly half of the more than 200 steel products in Germany are used. European standard, expected in another 5-6 years to reach European standards ENS 20, 000, which means that the standard DIN 23 000, 20, 000 is the result of good coordination in Europe.
 E hexagonal head and hexagon socket groove diagonal size e
The hexagonal opposite side s determines the specification of the mounting wrench, and whether the predetermined tightening torque can be achieved is determined by the diagonal point e of the force point . After the S size is determined, the max value of e is determined, so only the min value of e is specified in the standard.
 F anti- loose
There are three commonly used anti-loose methods: friction anti-loose, mechanical anti-loose and permanent anti-loose. Â Mechanical anti-loose and friction anti-loose are called detachable anti-loose, while permanent anti-loose is called non-removable anti-loose. Â Commonly used permanent anti-loose: spot welding, riveting, bonding, etc. This method mostly destroys the threaded fasteners during disassembly and cannot be reused. Â Common friction anti-loose: use gaskets, self-locking nuts and double nuts. Â Common mechanical anti-loose methods: the use of split pins, stop pads and string wire ropes. Â The method of mechanical anti-loose is relatively reliable, and mechanical anti-loose methods are used for important joints.
 G G B , G B/T
GB China National Standard, compulsory execution; GB/T China national standard, non-mandatory standard, recommended implementation.
 H H RC
Rockwell Hardness ( HR ) Test When the sample being tested is too small or the Brinell hardness ( HB ) is greater than 450 , it is measured by Rockwell hardness. The test method is to use a diamond cone with a apex angle of 120 degrees or a steel ball with a diameter of 1.59 mm/3.18 mm , and press it into the surface of the material to be tested under a certain load, and the hardness of the material is determined from the depth of the indentation . HRC Â It is a hardness obtained by using a 150Kg load and a diamond cone indenter for materials with high hardness.
 I I SO
ISO standard refers to standard by the "International Organization for Standardization (International Organization for Standardization, ISO)" developed. The International Organization for Standardization is a worldwide federation of national standardization bodies with 140 member states.
The predecessor of ISO was the International Standardization Association ( ISA ). The ISA was established in 1926. (In 1926 , the third meeting of the three representative organizations of the United States, Britain, and Canada decided to establish the International Standardization Association and was established in 1928 ). The outbreak of the Second World War forced ISA to stop working. After the war, the environment provided conditions for industrial recovery. In October 1946 , leaders from 25 national standardization bodies met in London to discuss the establishment of the International Organization for Standardization and called the new organization ISO . Abbreviation for International Organization for Standardization . The meeting unanimously passed the ISO regulations and rules of procedure. February 23, 1947 ISO began formal operation, the central ISO offices in Geneva, Switzerland. China is both a sponsor and a member of the first group.
      J impact test
Impact testing is generally a test method for determining the safety , reliability, and effectiveness of military and civilian equipment when subjected to external impact or action . Impact tests are related to notches, temperatures, etc. When the metal material is in a low temperature environment, its strength and bearing capacity will decrease, resulting in brittleness. Therefore, it is necessary to do a low temperature impact test; if it is considered that the winter use environment reaches -20 °C , a low temperature impact test of -20 °C is required ; if winter The use environment may reach  -40 °C , then a low temperature impact test of -40 °C must be performed .
 K K S
Ks , Korean standard, and Japanese standard JIS have many similarities, such as: Phillips screws as a category, such that Phillips pan head screws, cross recessed countersunk screws, etc. have a common standard code. The seventh edition of "Fasteners Daquan" has more demonstrations on the KS Korean standard.
 L length ( L )
In the standard of screws and bolts, the nominal length L is a main parameter for specifying the specific specifications; when mated with the internally threaded fastener, the threaded mating length determines the force effect of the thread.
 M riveting
Riveting is a mechanical vocabulary that uses rivets to join two or more pieces of work, such as a hole in a shoe that is laced, or a hollow rivet.
1. Activity riveting. The coupling members can rotate relative to each other. Not a rigid connection. Such as: scissors, pliers.
2. Fixed riveting. The joints cannot move with each other. This is a rigid connection. Such as: square ruler, nameplate on the three-ring lock , bridge construction.
3. Seal riveting. The rivet joint is tight and does not leak gas or liquid. This is a rigid connection.
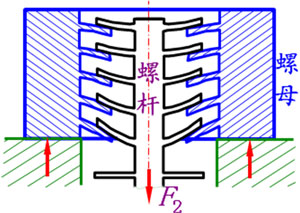
 N nut thickness ( N ut )
The thickness of the nut determines the number of threads that the nut has. The above figure shows the force of the threads of each ring after the bolt and nut are combined with the force.
Â
O semi-submerged head ( O )
Abbreviation for semi-submerged head type in the Pearl River Delta region P pan head ( P )
Abbreviation for Pantou Head Type in the Pearl River Delta Region
Q steam standard ( QC/T )
In order to ensure the quality of automotive products, especially in order to meet the requirements of safety, environmental protection and energy conservation, and promote the serialization, generalization and standardization of automobile production, countries have formulated a series of automotive standards, as automobile manufacturers, Guidelines that vendors and users must follow together. Domestic automotive fastener standard QC/T
 R round chamfer r
The r round chamfer below the receiving surface causes the chamfered portion to sink into the hole and form a dangling; the small one will cause the fastener product to be broken when subjected to a variable load.
 S to the side s
Hexagonal, etc. on the side dimension s wrenching tool determines the size specifications, s is too large, the use of wrenching tools can not be inserted; s too small, making it impossible to achieve sufficient tightening torque slip phenomenon.
 T T head
T -head bolts and nuts are often used in similar grooves in the Hafen groove to prevent rotation.
 U U -shaped bolt
U -bolt, that is, riding bolts, Â The English name of the riding bolt is U-bolt , the shape is U -shaped, so it is also called U -bolt. The two ends are threaded and can be combined with the nut. It is mainly used to fix tubular objects such as water pipes or sheets, such as leaf springs of automobiles. The way to fix objects is like riding a horse on the horse, so it is called a horse riding bolt.
 V Vickers hardness ( H V )
With a load of 49.03~980.7N , the surface of the square tapered diamond presser with a relative angle of 136° is pressed, and after maintaining the specified time, the length of the diagonal of the indentation is measured, and then the hardness is calculated according to the formula. . It is suitable for the hardness measurement of larger workpieces and deeper surface layers . Vickers hardness still has small load Vickers hardness, test load 1.961~<49.03N , it is suitable for hardness measurement of thin workpiece, tool surface or coating; micro Vickers hardness, test load <1.961N , suitable for metal foil Determination of the hardness of the extremely thin surface layer.
 W tungsten ( W )
The main use of tungsten in steel is to increase tempering stability, red hardness, heat strength, and increased wear resistance due to the formation of tungsten carbide.
 X milling machine
A milling machine is a machine tool that mainly uses a milling cutter to machine various surfaces on a workpiece. Usually, the rotary motion of the milling cutter is the main motion, and the movement of the workpiece ( and ) milling cutter is the feed motion. It can process flat, vertical, beveled, various grooves (such as keyways) or molding surfaces. If equipped with accessories (such as indexing head), it can also process spiral grooves, cams, forming surfaces, etc.
 Y Hardness
Hardness, the ability of a material to partially resist the pressing of a hard object into its surface is called hardness. The local resistance of solids to external objects is an indicator of the softness and hardness of various materials. Since different test methods are specified, there are different hardness standards. The mechanical meanings of various hardness standards are different and cannot be directly converted to each other, but can be compared by experiments. As early as 1822 , Friedrich mohs proposed using 10 minerals to measure the world's hardest and softest objects, the so-called Mohs hardness tester.
 Z maximum value / minimum value
In fasteners, the upper and lower limits of the standard range are usually specified by max max and min min . Between the measurement values of max and min values are Eligible.
This article is easy to tighten the original fastener network, welcome to reprint!
Reprinted must indicate the source of the article: easy to tighten fastener network
Lap Joint Flanges (LJ Flanges) are used on piping fitted with lapped pipe or with lap joint stub ends the combined initial cost of the two items being approximately one-third higher than that of comparable Welding Neck Flanges.
Lap joint flange is having two components, a stub end, and a loose backing flange. Stub end is butt welded to the pipe and Backing flange freely move over the pipe. The backing flange can be of different material than stub material and normally of the carbon steel to save the cost. Lap flange is used where frequent dismantling is required, and space is constrained.
Furthermore, a standard lap joint flange will typically have a longer hub length in comparison to a slip on flange, but this is often considered unnecessary for many applications.
The lap joint flange is practically identical to a slip-on flange except it has a radius at the intersection of the bore and flange face.
Lapped Flange,Joint Flange,Lap Joint Flange,LJ Flange
Shandong Zhongnuo Heavy Industry Co.,Ltd. , https://www.zhongnuoflanges.com